Ultimate Guide to Pressure Relief Valve Selection and Maintenance Tips
In the realm of industrial safety and equipment management, the selection and maintenance of a pressure relief valve (PRV) is paramount. Industry studies, such as the 2023 report by the Pressure Relief Valve Association, highlight that over 50% of equipment failures are attributable to improper valve maintenance. This underscores the importance of a comprehensive understanding of the 1 pressure relief valve and its critical role in safeguarding against hazardous overpressure conditions.
Furthermore, renowned expert in pressure systems, Dr. James Armitage, emphasizes, “The effectiveness of any pressure relief system hinges on the proper selection and ongoing maintenance of the valves involved.” This statement resonates with the increasing need for industries to prioritize not only the initial choice of a pressure relief valve but also its longevity and operational reliability through diligent maintenance practices.
In this ultimate guide, we will delve into the essential criteria for selecting the right 1 pressure relief valve, alongside practical maintenance tips to ensure optimal performance, drawing insights from industry standards and expert recommendations. By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can significantly mitigate risks, enhance safety, and ultimately protect both personnel and equipment from the disastrous consequences of pressure system failures.
Understanding Pressure Relief Valves: Types and Applications
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) are essential components in various industries, serving as safety devices that prevent overpressure conditions that could lead to catastrophic failures. The two main types of PRVs are conventional spring-loaded valves and pilot-operated valves. Conventional valves are most commonly used for liquid applications because of their simplicity and reliability, while pilot-operated valves are preferred in gas applications due to their higher accuracy and flow capacity. According to a recent industry report, the global pressure relief valve market is projected to reach $5.4 billion by 2027, driven by increasing safety regulations and the growing demand in oil and gas industries.
When selecting a PRV, it's crucial to consider the specific application, including the medium, pressure range, and temperature conditions. Always ensure that the selected valve complies with industry standards such as ASME and API. Additionally, conducting a thorough analysis of potential maintenance needs can enhance the longevity and efficiency of the valve.
**Tips:** Regular inspection of PRVs is vital. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, and proper seating. Schedule maintenance during non-peak operational hours to minimize downtime. Moreover, training staff on the proper operational protocols ensures that the valves effectively maintain pressure limits without unnecessary wear. By keeping a detailed maintenance log, facilities can better anticipate future needs and avoid unexpected failures.
Key Standards and Regulations Governing Pressure Relief Valve Design

When it comes to the design and application of pressure relief valves (PRVs), adherence to key standards and regulations is crucial for ensuring safety and operational efficiency. Various organizations provide guidelines that inform the design criteria for PRVs, ensuring they can effectively prevent overpressure scenarios in industrial systems. Notably, standards set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) are widely recognized within the industry. These standards dictate parameters such as sizing, testing, and installation, ensuring that the valves operate reliably under intended service conditions.
In addition to ASME and ANSI standards, organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) contribute to the establishment of global benchmarks for PRV design. Compliance with ISO standards not only enhances safety but also facilitates international trade by providing assurance of quality and performance. Furthermore, regulatory authorities such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) emphasize the importance of maintaining PRVs in compliance with these standards. Regular inspections and maintenance practices are essential, as they ensure that PRVs remain functional and safe, thereby reducing the risk of catastrophic failures in processing environments.
Factors Affecting Pressure Relief Valve Selection for Different Industries
When selecting a pressure relief valve (PRV), various factors come into play that differ across industries. Primarily, the operational conditions, including temperature, pressure, and the types of fluids involved, are crucial. For instance, in the oil and gas sector, valves must withstand extreme pressures and corrosive environments, necessitating materials that offer high strength and resistance to chemical degradation. In contrast, the food and beverage industry requires PRVs that adhere to strict sanitary standards, focusing on ease of cleaning and the prevention of contamination.
Another significant aspect to consider is the industry regulatory standards. Different sectors are governed by specific codes and regulations that dictate the required specifications for PRVs. For example, the pharmaceutical industry often demands valves that can operate reliably under high purity conditions, while also providing documentation for compliance. Additionally, the safety practices of each sector influence the design and maintenance of PRVs, with industries like mining placing a heightened emphasis on failsafe mechanisms to avert catastrophic failures. Selecting a valve that aligns with these multifaceted industry requirements ensures optimal performance and safety reliability.
Maintenance Best Practices to Ensure Pressure Relief Valve Reliability
To ensure the reliability and efficiency of pressure relief valves, regular maintenance is crucial. One of the best practices is to implement a scheduled inspection routine, which allows for early identification of wear and tear. During inspections, it is essential to check for signs of corrosion, leakage, or blockages that could impede the valve's operation. Keeping a record of these inspections helps track performance trends and allows for timely interventions.
Additionally, training personnel on proper operating procedures is vital. Ensuring that those who interact with pressure relief valves understand the importance of these components can lead to more vigilant monitoring and quicker responses to potential issues. It is also beneficial to conduct regular testing of the valves to confirm their functionality under simulated conditions. This proactive approach not only extends the lifespan of the valves but also ensures that they perform effectively when needed, thus maintaining the overall safety and efficiency of the system.
Common Failure Modes of Pressure Relief Valves and Their Remedies
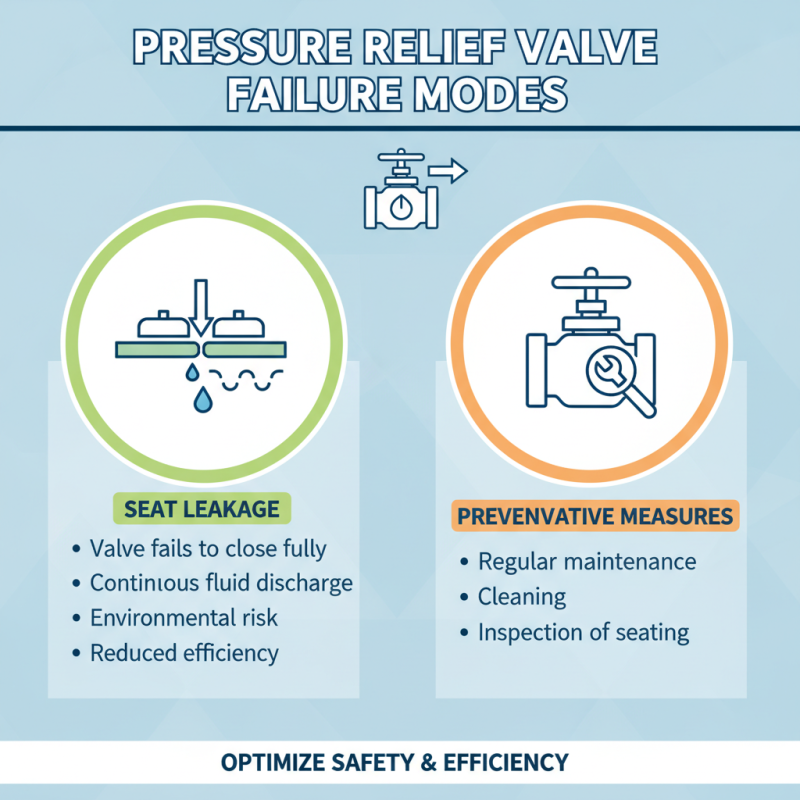
Pressure relief valves are critical components in various industrial systems, and they can experience several common failure modes that may compromise safety and efficiency. One prevalent issue is seat leakage, where the valve does not completely close after relieving excess pressure. This can lead to continuous discharge of fluid, which not only poses risks of environmental contamination but also affects the operational efficiency of the system. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspecting the valve's seating surface, can help mitigate this problem.
Another common failure is corrosion and erosion, often resulting from the harsh environments in which these valves operate. This can weaken the valve body and its components, leading to potential failure under pressure. Implementing proper material selection and regular inspections allows for early detection of wear, thus enabling timely replacements or repairs. Moreover, maintaining appropriate system conditions, such as temperature and fluid composition, can significantly reduce the likelihood of corrosion and prolong the lifespan of the pressure relief valve.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Role of Temperature and Pressure Relief Valves: Key Data and Insights for Safety Compliance
-

Best Watts Pressure Relief Valve Options for Optimal Safety and Efficiency
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Pressure Release Valve
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Inline Pressure Relief Valves in Your System
-

5 Best Pressure Vacuum Relief Valves for Optimal Safety and Performance in 2023
-

2025 Top 5 Safety Relief Valve Innovations You Should Know
